
Have you ever heard about block chain? If not, then you must have heard about Bitcoin. If you know about Bitcoin, it will be easier for you to understand blockchain. The record keeping of Bitcoin is called block chain. Apart from Bitcoin, block chain is also related to banking and investment firms.
understand block chain properly — what it really is.

is a database. So, what is a database? A database is a collection of information that is stored electronically on a computer system. In a database, information is organized in a table format so that specific data can be easily searched and filtered. A database can be used by multiple users at the same time. The main aim of blockchain is to digitally record all data.
This concept of data first came to light in 1991 through Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta.
The first launch of block chain, or you can say its first appearance, was in 2009 — along with Bitcoin.
Why is it called block chain?
Block chain collects information in groups, and these groups are called blocks. Each block has a limited capacity or storage. When it becomes full, it gets linked to the previously filled block, forming a chain of data. That’s why it is called a block chain.
Element of Block Chain and Way of Work
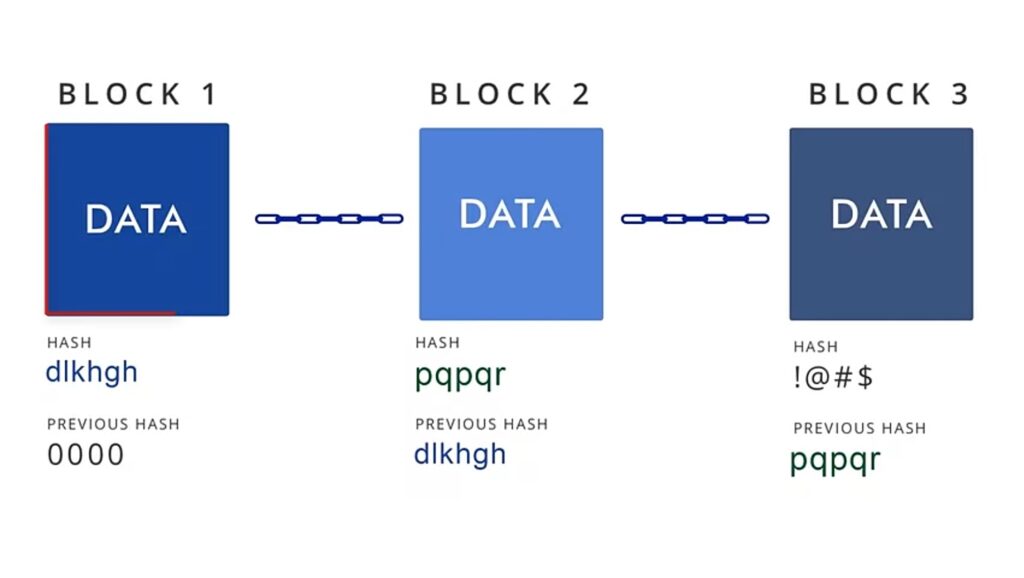
Block chain is a type of chain that contains information. Each block in the chain contains the cryptographic hash of the previous block. This hash is generated for every transaction, and it is a string of numbers and letters.
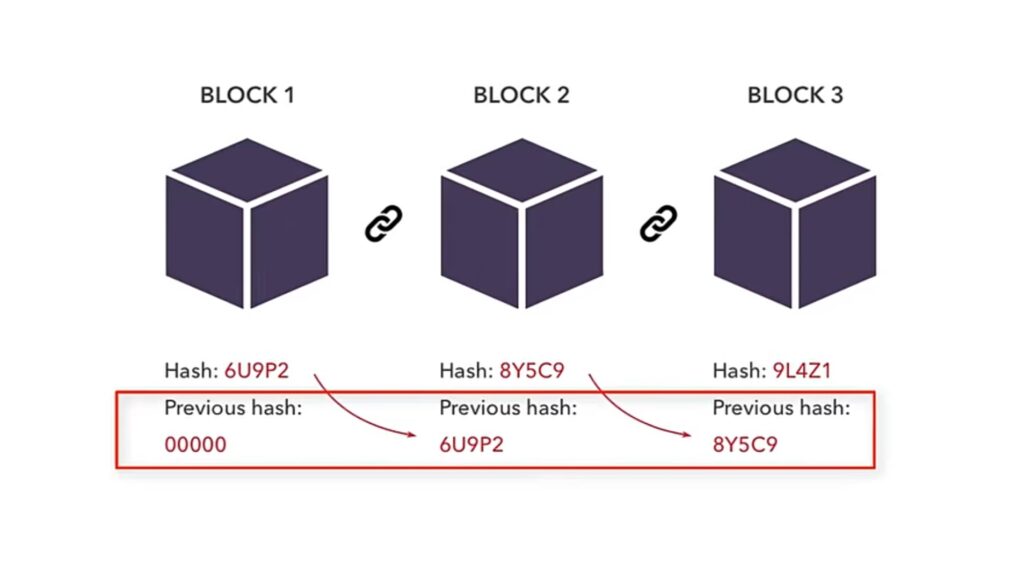
This hash is generated for every transaction, and it is a string of numbers and letters. This hash does not depend only on the transaction itself, but also on the hash of the previous transaction in the chain.
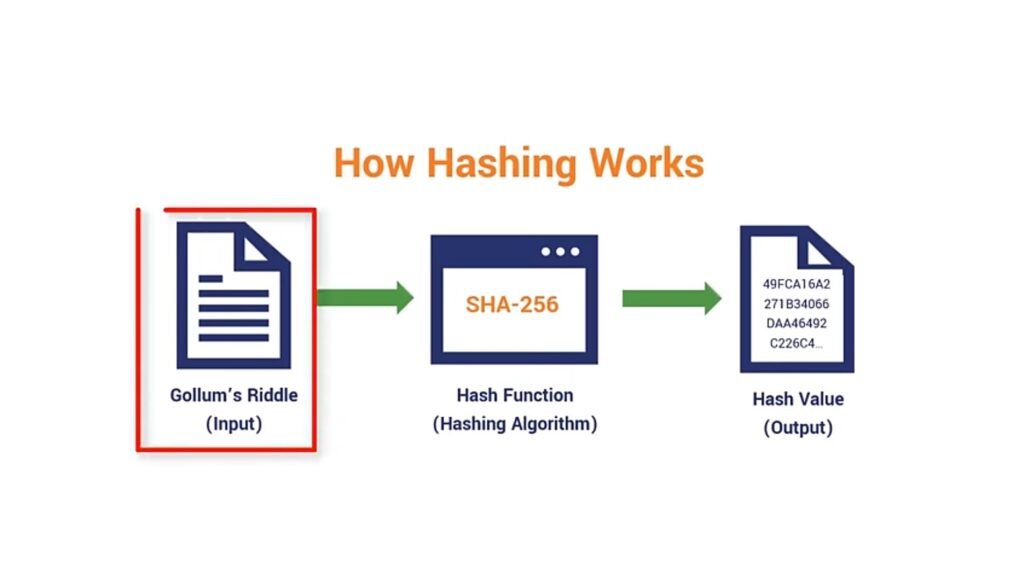
If even the smallest change is made in a transaction, a new hash is generated. This means that if anyone tampers with the data in the blockchain, all the related data changes, making it easy to detect any alterations in the records. That’s why it is considered a secure option. Block chain is spread across many computers, and each computer holds a copy of the data. These computers are called nodes. These nodes check the hashes to determine whether any changes have been made in a transaction. When a node approves a transaction, it gets added to a block. These nodes form the infrastructure of the blockchain. They store, spread, and preserve the blockchain data. A full node is a computer that holds a complete copy of all blockchain transactions. The blockchain updates itself every 10 minutes.
How is blockchain useful for Bitcoin?

For Bitcoin, blockchain is a specific database that stores every transaction for each Bitcoin. It distributes Bitcoin’s cryptocurrency across computers, allowing you to operate it without the help of any central authority.
In Bitcoin, the blockchain stores and monitors the transaction data.
Blockchain is reliable for storing other types of data as well, such as in the finance sector, investment institutions, healthcare institutions, and so on.

Generally, banks take 5 days, so if you deposit a cheque, it takes around 2 days to clear. However, if you use integrated banking, it can be done in just 10 minutes.
With the help of blockchain, you can transfer funds. Even if the transfer is between two different institutions, it can be done using blockchain.

In healthcare, it can store a patient’s medical reports. For example, when a patient comes in for a checkup or is admitted, their records can be saved on the blockchain. If the same patient returns later, you can pull up their previous reports by searching their name or mobile number.

Blockchain is also used in voting and supply chains. It helps prevent election fraud. If any tampering occurs, it can be detected with the help of blockchain.

Benefits of Blockchain:
Security: Data is encrypted and tamper-proof, making it highly secure.
Transparency: All transactions are visible to authorized participants, reducing fraud.
Decentralization: No single authority controls the network, increasing trust.
Faster Transactions: Transfers and settlements happen much quicker than traditional systems.
Data Integrity: Once recorded, data cannot be easily altered or deleted.
Wide Applicability: Can be used in banking, investments, healthcare, supply chain, voting, and more.
Multi-User Access: Multiple users can access and verify data simultaneously
Disadvantages of Blockchain:
High Energy Consumption: Many blockchains, especially those using proof-of-work, consume a lot of electricity.
Scalability Issues: As more transactions occur, the system can become slower and require more storage.
Complexity: Understanding and implementing blockchain technology can be difficult for beginners.
Irreversible Transactions: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be undone, which can be risky in case of errors.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Blockchain and cryptocurrencies face unclear or evolving legal regulations in many countries.
Cost: Setting up and maintaining blockchain networks can be expensive.
Limited Adoption: Despite its benefits, blockchain is not yet widely adopted in all sectors.